The Rise of Smart Cities
A smart city is a city that uses technology and data-driven solutions to efficiently manage growing urbanization, energy consumption, maintain a green environment, improve the economic and living standards of its citizens, and raise the people’s capabilities to efficiently use and adopt modern information and communication technology (ICT). To make lifestyles in cities more comfortable and cost-effective, cities must be both smart and considerate, placing sufficient importance on key stakeholders, particularly citizens and technological enablers. In earlier articles, we discussed the vital role of citizens as stakeholders. Here, we turn our attention to the technological dimension, emphasizing how artificial intelligence, for instance, can support intelligent decision-making through technologies grounded in computational intelligence.
In the smart city framework, technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and deep reinforcement learning (DRL) play an essential role in policy design, implementation, and service optimization. These tools are critical for addressing complex urban challenges through efficient and scalable solutions.
AI in Smart Cities
As defined by computer scientist John McCarthy (1979), AI is “the science and engineering of making intelligent machines.” In smart cities, real-time data analysis by AI can assist urban planners to optimize traffic flows using sensor and camera data to reduce congestion, or manage energy consumption dynamically based on building occupancy patterns. In addition, it enhances public services through data-driven decision-making. AI acts as the backbone of smart cities, simulating human-like judgment to automate tasks and improve efficiency.
IoT and Big Data: AI’s Fuel
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the pillar of smart city applications, generating massive datasets. Given the volume and complexity of this data, it’s difficult to precisely decide the most accurate and efficient actions. Advanced techniques like artificial intelligence can analyze large-scale data effectively to support optimal decision-making. AI is essential for extracting meaningful insights from IoT-generated data.
AI is also being used to create more responsive and personalized services for residents. For example, chatbots and virtual assistants can provide personalized information and support to citizens, while predictive analytics can help city agencies identify and address issues before they become problems.
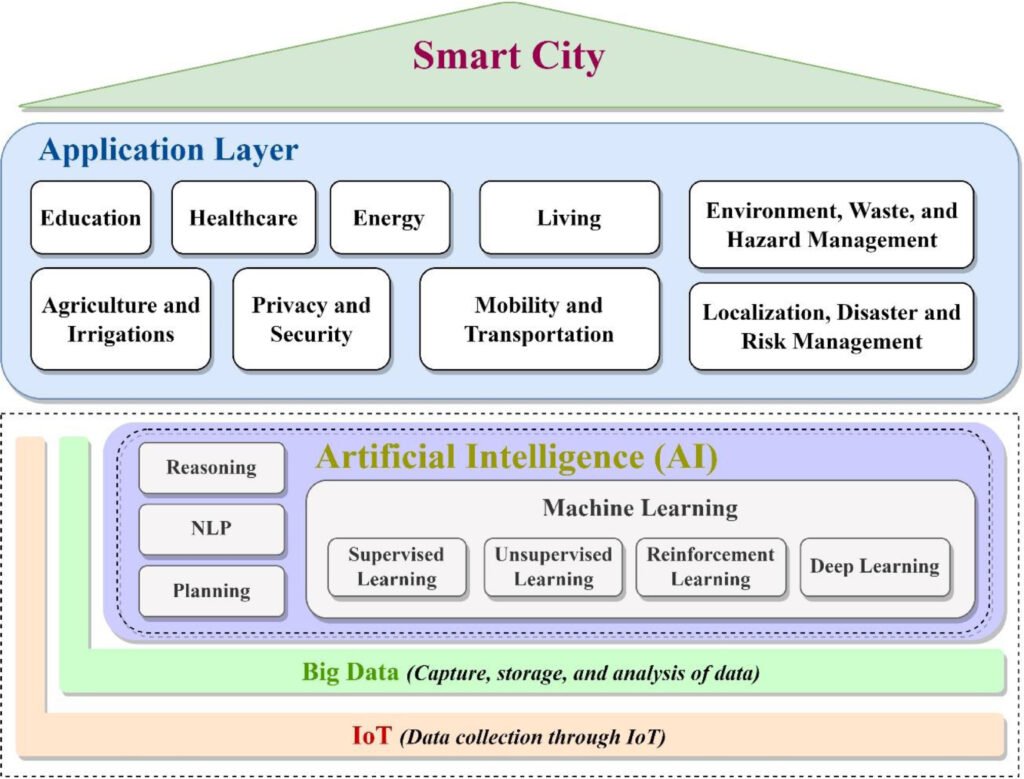
AI Across Smart City Sectors
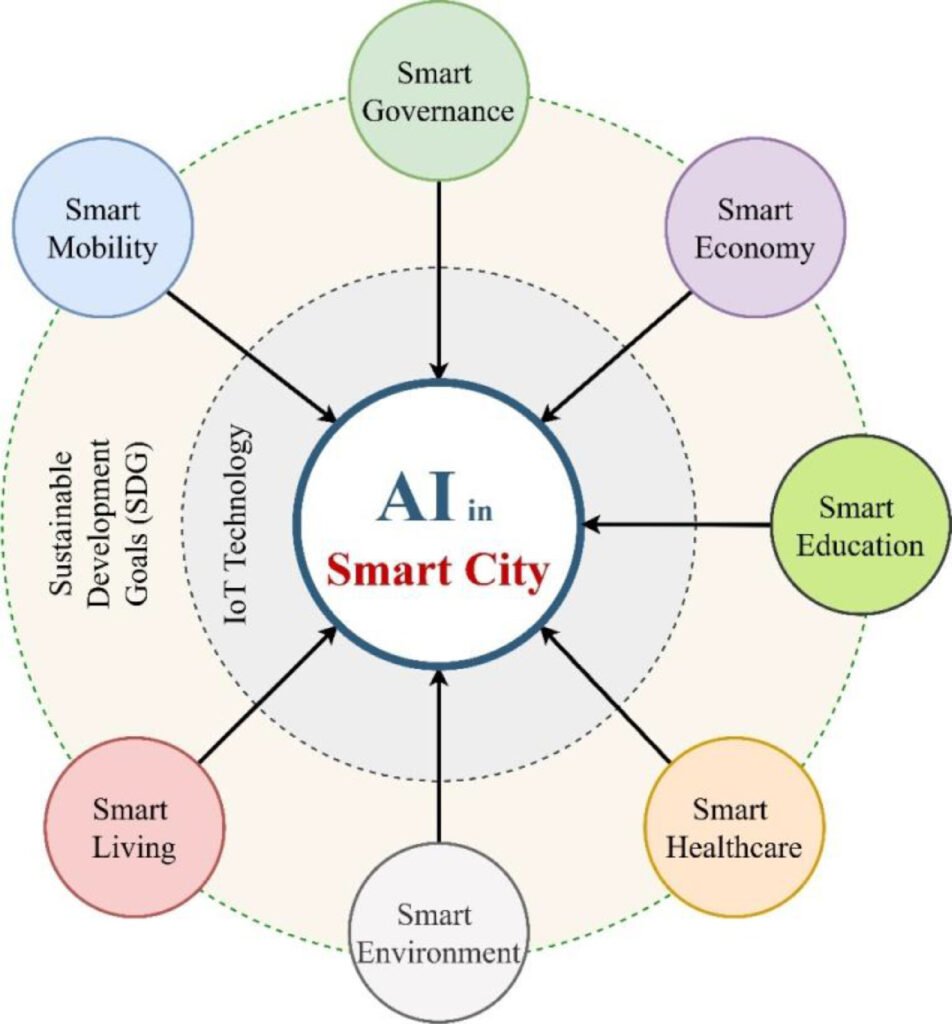
In smart city projects, various sectors like Intelligent transportation, cyber-security, smart grids (SGs), and UAVs assisted next-generation communication (5G and B5G), etc. are playing a vital role. All the preceding sectors of a smart city is highly influenced by Big data analytic and effective use of AI, and other analytics techniques that can enhance their efficiency and scalability in a smart city project. AI can be used in various domains of smart cities, like: Smart Mobility, smart education, smart healthcare, smart environment, smart living & infrastructure, economy and smart governance.
The Impact of AI: Opportunities and Challenges
The impact of AI on our daily life activities is increasing day by day. AI is rapidly changing the nature of our daily jobs, impacting the traditional approach of human thinking, and interaction with the environment. How should the new regulations be designed to safeguard the current and future generations from the negative aspects of AI and maximize its positive impacts over humanity? Moreover, how AI-assisted policies and regulations should be developed to ensure social and economic development. However, there are also concerns about the impact of AI on privacy and security in smart cities, and the potential for AI to exacerbate existing inequalities if not carefully designed and implemented. Therefore, it is important to ensure that smart city projects are designed with ethical considerations in mind, and that they are developed in collaboration with citizens and other stakeholders to ensure that they meet their needs and aspirations.
Conclusion
As smart cities evolve, emerging technologies such as AI, IoT, and blockchain will unlock transformative opportunities; from AI-powered climate resilience systems that combat urban heat islands to autonomous public transport optimizing mobility in real time. Further innovations like predictive infrastructure maintenance and personalized urban services will redefine urban living. However, ethical governance, robust data privacy, and inclusive design are essential to ensure equitable benefits for all citizens. The smart cities of tomorrow will flourish only by marrying technological advancement with human-centered priorities.
Pingback: Bridging Technology and Governance: AI Solutions for Public Sector Transformation - most4tech.com